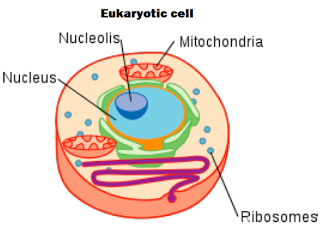
Within its cell wall and membrane, a plant cell has two basic parts called the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cell nucleus contains tiny threads called chromosomes.
Chromosomes carry the plant’s genes, the basic units of heredity. The first description of a subcellular structure termed “the nucleus” can be found in a paper first delivered to the Linnean Society of London on November of 1831.
The shape of the nucleus may be related to that of the cells or may be completely irregular. In spheroidal, cuboidal or polyhedral cells, the nucleus is generally a spheroid. In cylindrical, prismatic, or fusiform cells, it tends to be an ellipsoid.
The nucleus occupies about 10% of a eukaryotic cell’s volume, In general, each somatic nucleus has a specific size that depends partly on its, DNA content and mainly on its protein content and so its size is related to functional activity during the period of nondivision.
Nucleus serves two important functions. First, it keeps the cell’s genetic material – its DNA – safe and sound. Isolated in its own compartment, the cell’s DNA stays separated from the
bustling activity of the cytoplasm and from metabolic processes that
might damage it.
Nucleus in plant cells
Allicin: The Key Bioactive Compound Behind Garlic’s Health Benefits
-
Allicin, a sulfur-containing compound derived from the amino acid alliin,
is one of the primary reasons garlic has earned its long-standing
reputation as b...